Introduction to ML
인프런 머신러닝과 딥 러닝 강좌를 듣고 정리 한 것입니다.
Tensorflow 기본적인 operations
pip3 install --upgrade tensorflow
# or
pip3 install --upgrade tensorflow-gpu
import tensorflow as tf
tf.__version__
hello = tf.constant("Hello World!")
sess = tf.Session()
print(sess.run(hello))
n1 = tf.constant(3.0, tf.float32)
n2 = tf.constant(4.0)
n3 = tf.add(n1, n2)
sess.run([n1, n2])
sess.run(n3)
Placeholder
a = tf.placeholder(tf.float32)
b = tf.placeholder(tf.float32)
adder_node = a + b
sess.run(adder_node, feed_dict={a: 3, b: 4.5}))
# 7.5
sess.run(adder_node, feed_dict={a: [1,3], b: [2, 4]}))
# [ 3. 7.]
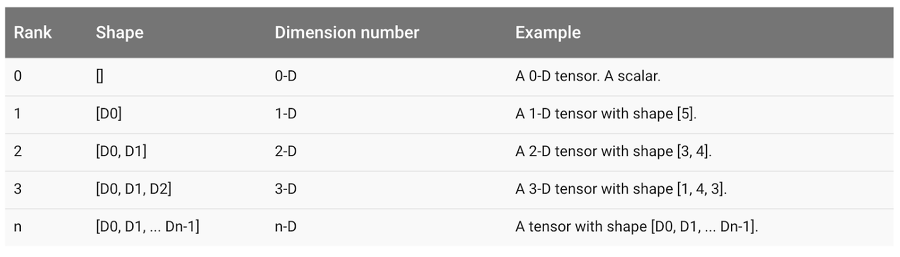
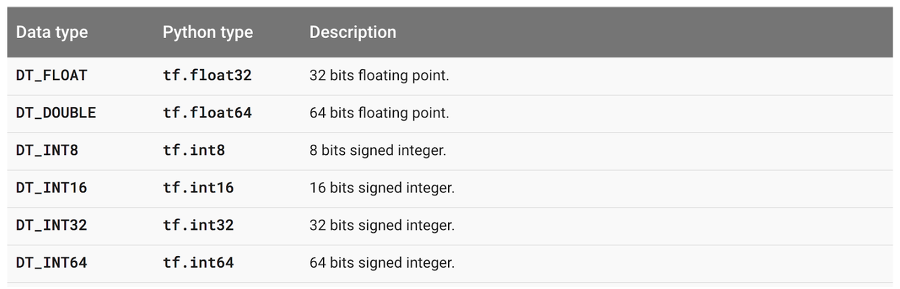
Type, Shape, Rank


Linear Regression
Hypothesis based on “H(x)=Wx+b”
Cost: (H(x)-y)^2
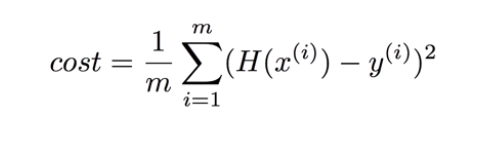
Goal: Minimize “cost(W,b)”
Linear Regression의 cost 최소화 알고리즘 원리
x = [1, 2, 3]
y = [2, 4, 6]
W = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([1]), name='weight')
b = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([1]), name='bias')
hypo = x*W+b
cost=tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(hypo-y))
optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate=0.01)
train = optimizer.minimize(cost)
sess = tf.Session()
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
for step in range(2001):
sess.run(train)
if step % 20 == 0:
print(step, sess.run(cost), sess.run(W), sess.run(b))
Placeholder로 해보기
X = tf.placeholder(tf.float32)
Y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32)
for step in range(2001):
cost_val, W_val, b_val, _ = \
sess.run([cost, W, b, train],
feed_dict={X: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5], Y: [2.1, 3.1, 4.1, 5.1, 6.1]})
if step % 20 == 0:
print(step, cost_val, W_val, b_val)